#include <diagnostic-path.h>
Data Structures | |
| struct | meaning |
Public Types | |
| enum class | verb { unknown , acquire , release , enter , exit , call , return_ , branch , danger } |
| enum class | noun { unknown , taint , sensitive , function , lock , memory , resource } |
| enum class | property { unknown , true_ , false_ } |
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual | ~diagnostic_event () |
| virtual location_t | get_location () const =0 |
| virtual int | get_stack_depth () const =0 |
| virtual void | print_desc (pretty_printer &pp) const =0 |
| virtual logical_location | get_logical_location () const =0 |
| virtual meaning | get_meaning () const =0 |
| virtual bool | connect_to_next_event_p () const =0 |
| virtual diagnostic_thread_id_t | get_thread_id () const =0 |
| virtual void | maybe_add_sarif_properties (sarif_builder &, sarif_object &) const |
| virtual std::unique_ptr< diagnostics::digraphs::digraph > | maybe_make_diagnostic_state_graph (bool debug) const |
| label_text | get_desc (pretty_printer &ref_pp) const |
Detailed Description
A diagnostic_path is an optional additional piece of metadata associated
with a diagnostic (via its rich_location).
It describes a sequence of events predicted by the compiler that
lead to the problem occurring, with their locations in the user's source,
and text descriptions.
For example, the following error has a 3-event path:
test.c: In function 'demo':
test.c:29:5: error: passing NULL as argument 1 to 'PyList_Append' which
requires a non-NULL parameter
29 | PyList_Append(list, item);
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
'demo': events 1-3
25 | list = PyList_New(0);
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~
| |
| (1) when 'PyList_New' fails, returning NULL
26 |
27 | for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
| ~~~
| |
| (2) when 'i < count'
28 | item = PyLong_FromLong(random());
29 | PyList_Append(list, item);
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
| |
| (3) when calling 'PyList_Append', passing NULL from (1) as argument 1
The diagnostic-printing code has consolidated the path into a single
run of events, since all the events are near each other and within the same
function; more complicated examples (such as interprocedural paths)
might be printed as multiple runs of events. Abstract base classes, describing events within a path, and the paths themselves.
One event within a diagnostic_path.
Member Enumeration Documentation
◆ noun
|
strong |
◆ property
|
strong |
◆ verb
|
strong |
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ ~diagnostic_event()
|
inlinevirtual |
Member Function Documentation
◆ connect_to_next_event_p()
|
pure virtual |
◆ get_desc()
| label_text diagnostic_event::get_desc | ( | pretty_printer & | ref_pp | ) | const |
Generate a label_text containing the description of this event (for debugging/logging purposes).
References pretty_printer::clone(), pp_formatted_text(), pp_show_color(), and print_desc().
◆ get_location()
|
pure virtual |
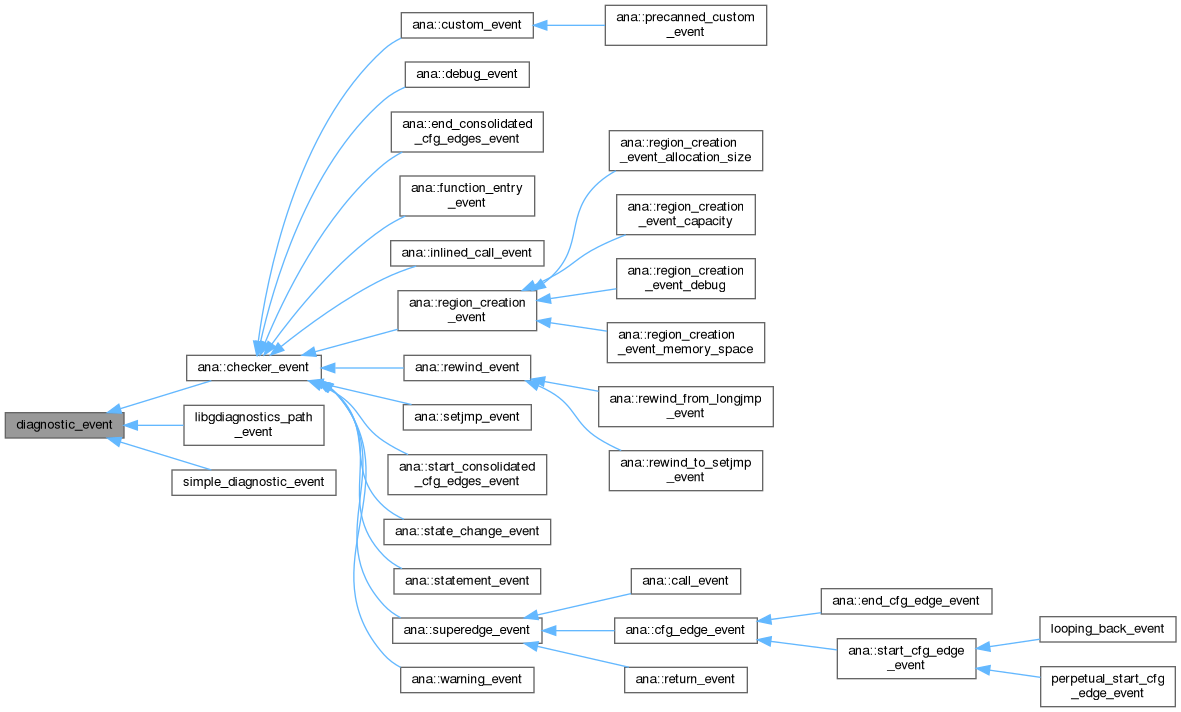
Implemented in ana::checker_event, libgdiagnostics_path_event, and simple_diagnostic_event.
◆ get_logical_location()
|
pure virtual |
Implemented in ana::checker_event, libgdiagnostics_path_event, and simple_diagnostic_event.
◆ get_meaning()
|
pure virtual |
Implemented in ana::call_event, ana::cfg_edge_event, ana::checker_event, ana::function_entry_event, ana::inlined_call_event, ana::return_event, ana::start_consolidated_cfg_edges_event, ana::state_change_event, ana::warning_event, libgdiagnostics_path_event, and simple_diagnostic_event.
Referenced by sarif_builder::populate_thread_flow_location_object().
◆ get_stack_depth()
|
pure virtual |
Implemented in ana::checker_event, libgdiagnostics_path_event, and simple_diagnostic_event.
Referenced by diagnostic_path::interprocedural_p(), and sarif_builder::populate_thread_flow_location_object().
◆ get_thread_id()
|
pure virtual |
Implemented in ana::checker_event, libgdiagnostics_path_event, and simple_diagnostic_event.
◆ maybe_add_sarif_properties()
|
inlinevirtual |
Reimplemented in ana::checker_event, and ana::superedge_event.
Referenced by sarif_builder::populate_thread_flow_location_object().
◆ maybe_make_diagnostic_state_graph()
|
virtual |
Reimplemented in ana::checker_event, and libgdiagnostics_path_event.
Referenced by sarif_builder::populate_thread_flow_location_object().
◆ print_desc()
|
pure virtual |
Implemented in ana::call_event, ana::catch_cfg_edge_event, ana::debug_event, ana::end_cfg_edge_event, ana::end_consolidated_cfg_edges_event, ana::explicit_throw_event, ana::function_entry_event, ana::inlined_call_event, ana::precanned_custom_event, ana::region_creation_event_allocation_size, ana::region_creation_event_capacity, ana::region_creation_event_debug, ana::region_creation_event_memory_space, ana::return_event, ana::rewind_from_longjmp_event, ana::rewind_to_setjmp_event, ana::setjmp_event, ana::start_cfg_edge_event, ana::start_consolidated_cfg_edges_event, ana::state_change_event, ana::statement_event, ana::throw_from_call_to_external_fn_event, ana::unwind_event, ana::warning_event, libgdiagnostics_path_event, looping_back_event, perpetual_start_cfg_edge_event, and simple_diagnostic_event.
Referenced by get_desc().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files: